11. Exception and File IO
Exception
Exception is a problem that arises during run-time. Let’s try the following example in code.
10 / 0
List<Integer> lst = null; int size = lst.size();
String s = "FOOBAR"; int i = Integer.parseInt(s);
Int[] a = {1, 2, 3}; System.out.println(a[3]);If there is no exception handling mechanism, when exception happens, the system basically crash. Therefore, we need to find a way to properly handle our exceptions, so we can find out the problem while keeping our application running.
035ND C01 L01 A16 EXCEPTION AND JAVA IO V2 (Post Launch) 1
Exception keywords:
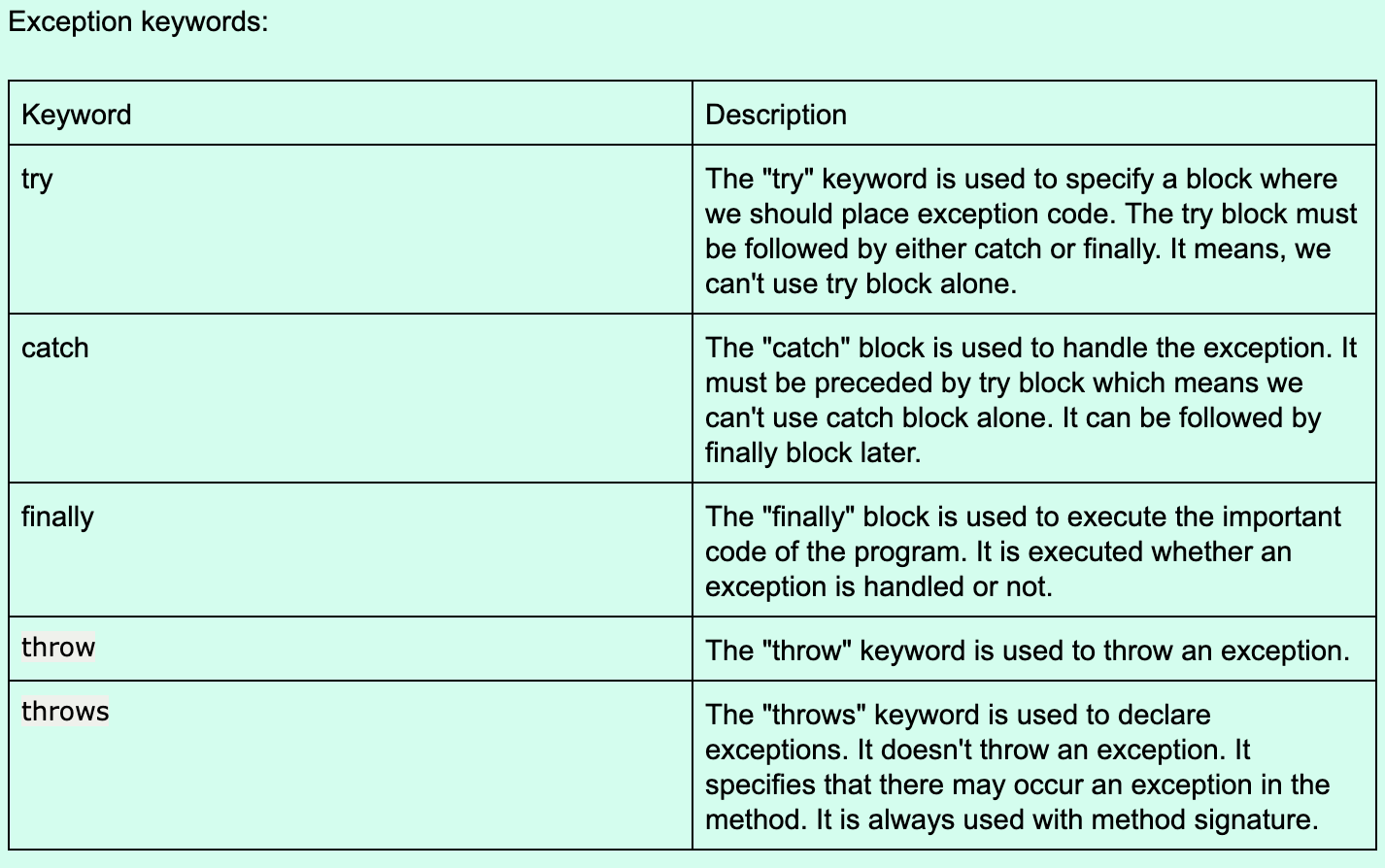
Create a program like
public class JavaExceptionExample{
public static void main(String args[]){
try{
//code that may raise exception
int data=100/0;
}catch(ArithmeticException e){System.out.println(e);}
//rest code of the program
System.out.println("rest of the code...");
}
} You will see that, you can see the error, but the rest of the code is still running. Add a final block as well.
035ND C01 L01 A17 EXCEPTION AND HANDLE EXCEPTION
Exception, Handle Exception Quiz
SOLUTION:
throwsException, Handle Exception Quiz 2
SOLUTION:
Throwable035ND C01 L01 A18 HOW TO HANDLE EXCEPTION CODE
035ND C01 L01 A19 EXCEPTION SUMMARY
File IO
Here we are going to cover Java.IO. Java IO is an API that comes with Java to read and write data. Most of the applications today support IO, for instance, ask user to upload a data feed, ask user to upload a photo, generate a PDF after user complete the form, grade students’ online exam and send the report as email.
IO Stream is like an endless flow of data. You can either read from a stream or write to a stream. A stream is connected to a data source or a data destination. Streams in Java IO can be either byte (reading and writing bytes) based or character based (reading and writing characters).
The File class in the Java IO API gives you access to the underlying file system. Using the File class you can:
- Check if a file or directory exists.
- Create a directory if it does not exist.
- Read the length of a file.
- Rename or move a file.
- Delete a file.
- Check if path is file or directory.
- Read list of files in a directory.
Resources:
Stream: https://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/api/java/util/stream/package-summary.html
File api: https://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/api/java/nio/file/Files.html
035ND C01 L01 A20 FILE IO, STREAMS, FILE APIS
File IO, Streams, File APIs Quiz
SOLUTION:
java.ioStream
Stream is like an endless flow of data. You can either read from a stream or write to a stream. A stream is connected to a data source or a data destination. Streams in Java IO can be either byte (reading and writing bytes) based or character based (reading and writing characters).
A program that needs to read data from some source needs an InputStream or a Reader. A program that need to write data to some destination needs an OutputStream or a Writer. Can show a graph like
[source] -> [input stream/reader] -> [program]
[program] -> [output stream/writer] -> [destination]
FileInputStream and FileOutputStream are common input and output stream classes. FileReader and FileWriter are common reader and writer classes.
We are going to be digging more in the next few videos
035ND C01 L01 A21 STREAM V@ (Post Launch) 1
FileInputStream
FileInputStream obtains input bytes from a file. It’s used for reading byte-oriented data such as image data, audio, videos. You can also read character-stream data. But, it’s recommended to use FileReader class to read character stream data.
Java FileOutputStream is an output stream used for writing data to a file. If you have to write primitive values into a file, use FileOutputStream class. You can write byte-oriented as well as character-oriented data through FileOutputStream class. But, for character-oriented data, it is preferred to use FileWriter than FileOutputStream.
FileReader is used to read character-oriented data from a file and FileWriter class is used to write character-oriented data to a file.
Resources:
FileInputStream: https://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/api/java/io/FileInputStream.html
FileOutputStream: https://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/api/?java/io/FileOutputStream.html
FileReader: https://docs.oracle.com/javase/9/docs/api/?java/io/FileReader.html
FileWriter: https://docs.oracle.com/javase/9/docs/api/?java/io/FileWriter.html
035ND C01 L01 A22 FILE INPUT
FileInputStream/FileOutputStream, FileReader/FileWriter Quiz
SOLUTION:
InputStreamFileReader and FileWriter Quiz
SOLUTION:
Yes. Some streams can be connected together.Buffer, BufferedReader
We’ve covered stream, inputstream, outputstream, filereader and filewriter. In this video we are going to learn Buffer and BufferReader.
Buffer is a region of a physical memory storage used to temporarily store data while it’s being moved from one place to another. The physical memory storage would be RAM in most case. For file IO, buffer is a storage stores part of the streamed data and feeds this to output.
When we use a buffer what happens is that each character is stored in the buffer first one by one in consecutive memory locations thus converting the stream of data into a single solid value.
Java BufferedReader class is used to read the text from a character-based input stream. It can be used to read data line by line by readLine() method, it can also be used to read data character by character by read() method. By sure to close bufferreader as well if you finish use it.
035ND C01 L01 A23 BUFFER V2 (Post Launch) 1
Resources:
BufferedReader: https://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/api/java/io/BufferedReader.html
Buffer Quiz